Accessibility Testing
European Accessibility Act (EU Directive 2019/882) came into effect at June 28, 2025. This legislation defines minimum accessibility standards for a wide range of products and services. In this post, we will look at available tools for accessibility testing and how to integrate them into your development process and how AutoExplore can play a role in this process.

Sampo Kivistö
Founder & CEO

The European Accessibility Act 2025
On June 28, 2025, the European Accessibility Directive EU Directive 2019/882 came into effect. The European accessibility act requires minimum accessibility standards for a wide range of products and services. It is aimed to ensure that people with disabilities can use products and services.
While the legislation is aimed at people with disabilities, it also impacts software programs and tools. In the AI era, where task automation is becoming more common, it is important to ensure that your web application is accessible.
Agents and Tools
Screen readers and basic web crawlers which are integrated into LLM often rely on the accessibility tree provided by the web browser. To make your application accessible, you need to make sure that the accessibility tree is correct. W3C provides an Accessibility Standard to help in building accessible websites and web applications.
Accessibility tree is used to tell information about the page. Incorrect accessibility tree can cause the following issues:
- Some part of the page is not "seen" by the assistive tool or agent. This can cause confusion or lose sales
- Test automation tools may not be able to interact with the page
- Some users may not be able to use the page and legal issues may arise
- Search engines may have less visibility due to missing information
- Bad user experience due to unclear or confusing UI, weird tab order, etc.
Accessibility Tree
You can access the accessibility tree in the browser developer tools. In FireFox you can open the accessibility tree by selecting Accessibility tab from the developer tools. In Chromium-based browsers, you can open the accessibility panel from the "Elements" panel and changing the view by clicking the "Accessibility" button.
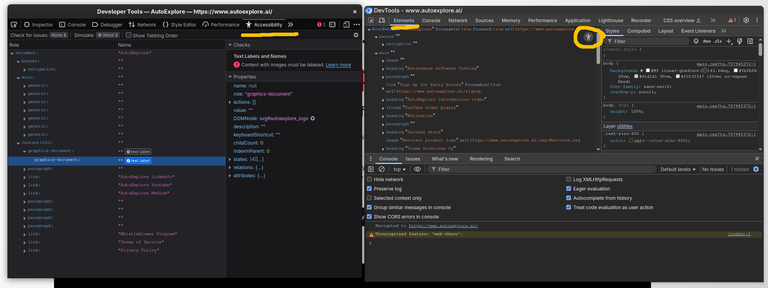
The browser accessibility tree view gives a quick look into the page and how it is structured and what information is available. You can also use FireFox accessibility tree for analyzing tab-order quickly.
There are also external tools that help you how to improve the accessibility of your web application during the development process.
You can integrate these tools into your browser for manual checks or playwright / cypress tests for tracking regressions.
One of the challenges with accessibility testing for modern web applications is that you always have to have the application in a specific state when scanning for accessibility issues. For example, to detect if your dropdown is accessible, you need to get the application into a state where the dropdown is visible, scan the application and then open the dropdown and scan again, then repeat this process for all the elements and pages.
In a recent AutoExplore update we added accessibility testing capabilities to our testing agent. This means when the agent browses the application, it is also continuously scanning for issues and reporting findings autonomously. It helps find edge cases that could be missed easily.
At AutoExplore, we are committed to helping R&D teams implement autonomous testing as part of their development processes. Ready to transform your process? Contact us for a demo to learn more.